backgroud
preivously, reviewed:
this blog is a little bit futher of vmware and AMD GPU virtualization sln.
AMD virtualization
S7150x2
for remote graphic workstation, usually we separate host machine and local machines, where host machine is located in data center, and local machines are the end-user terminals at offices.
the host OS can be Windows 7/8, Linux, and hypervisor can be vmware ESXi 6.0; guest os can be windows7/8, supported API includes: DX11.1, OpenGL
since S7150 has no local IO, os there is no display interface, just like a Nvidia Tesla GPU.
SR-IOV
- sr-iov arch
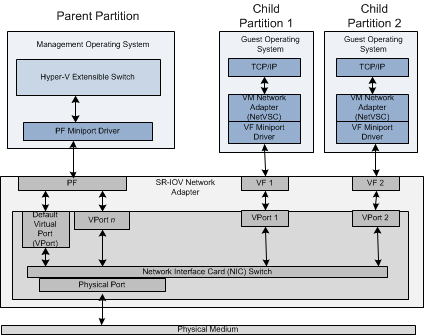
- Physical Function (PF)
it’s PCI-Express function of a network adapter that supports single root I/O virtualization(SR-IOV) interface. PF is exposed as a virtual network adapter(vLan) in the host OS, and the GPU driver in install in PF.
- Virtual Function (VF)
it’s a lightweight PCIe function on a network adapter that supports SR-IOV. VF is associated with the PF on the network adapter, and represents a virtualized instance of the network adapter. each VF has its own PCI configuration space, and shares one or more physical resources(e.g. GPU) on the network adapter.
- GPU SR-IOV
sr-iov basically split one PF(a PCIe resource) into multi VF(virtual PCIe resource). and each vf has its own Bus/Slot/Function id, which can used to access physical device/resources(e.g. GPU); Nvidia Grid vGPU is a different mechanism, where virtualization is implemented only in host machine side to assign device MAC address.
GPU resource managment
- display
GPU PF mangae the size of frameBuffer to each vf, and display virtualization.
- security check
PF also do an address audit check and security check
- VF schedule
GPU vf scheduler is similar as CPU process time-split. in a certain time period, the gpu is occupied by a certain vf.
Multiuser GPU(MxGPU)
AMD MxGPU is the first hardware-based virtualized GPU solution, based on SR-IOV, and allows up to 16 vm per GPU to work remotely.

now we see two GPU virtualization solutions:
|
|
vGPU is more software-based virtualization, but the performance is a little better; while MxGPU is hardware based.
vmware products
the license-free products, e.g. vSphere Hypervisor, VMware Remote Console
the licensed and 60days-free products, e.g. vSAN, Horizon 7, vSphere
vSphere
vSphere is the virtualization(hypervisor) layer of vmware products. there are two components: ESXi and vCenter Server. exsi is the core hypervisor, and vcenter is the service to mange multi vm in a network and host resources pool.
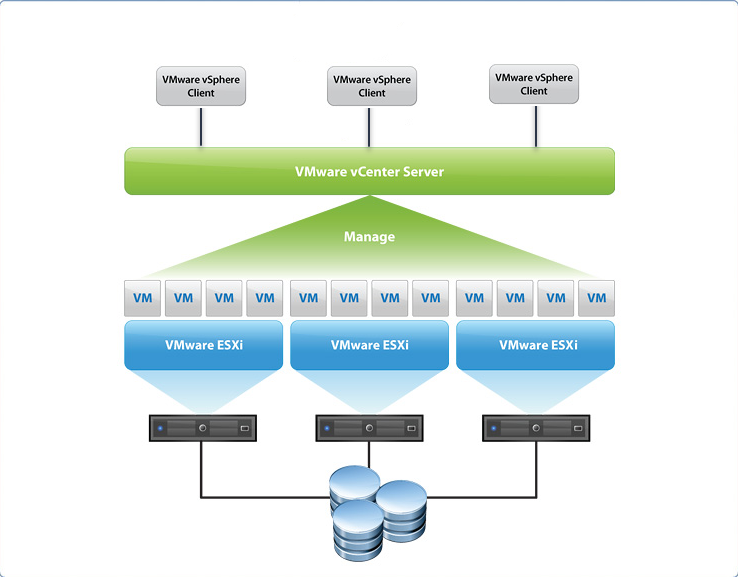
install and setup
a few steps including:
install ESXi on at least one host, either interactively or install through vSphere auto deploy, which include vServer. basically,
esxiis free, and can be install on system as the hypervisor layer for any future vms.setup esxi, e.g. esxi boot, network settings, direct console, syslog server for remote logging
deploy or install vCenter and services controller
Horizon

client devices
Horizon client
the client software for accesing remote desktops and apps, which will run on client devices. after logging in, users select from a list of remote desktops and apps that they are authorized to use. and admin can configure Horizon client to allow end users to select a display protocol.
- Horizon agent
it’s installed on all vms, physical machines, storage server that used as sources for remote desktops and apps. if the remote desktop source is a vm, then first need install Horizon Agent service on that vm, and use the vm as a tepmplate, when create a pool from this vm, the agent is automatically installed on every remote desktop.
- Horizon admin
used to configure Horizon connection server, deploy and manage remote desktops and apps, control user authentication e.t.c.
- Horizon connection server
serve as a broker for client connections.
a rich user experience
- usb devices with remote desktops and apps
basically can configure the ability to use USB devices from virtual desktop
- real-time video for webcams
basically can use local client(end-user terminal)’s webcam or microphone in a remote desktop or published app.
- 3d graphics
with Blast or PCoIP display protocol enable remote desktop users to run 3D apps, e.g. google earch, CAD.
vSphere 6.0+ supports NVIDIA vGPU, basically share GPU among vms, as well as support amd GPU by vDAG, basically share gpu by making GPU appear as multiple PCI passthrough devies.
desktop or app pool
first create one vm as a base image, then Horizon7 can generate a pool of remote desktops from the base image. similar for apps.
the benefit of desktop pool, if using vSphere vm as the base, is to automate the process of making as many identical virtual desktops as need, and the pool has manage tools to set or deploy apps to all virtual desktops in the same pool. for user assignment, either dedicated-assignment pool, which means each user is assigned a particular remote desktop adn returns to the same v-desktop at each login. it’s a one-to-one desktop-to-user relationship; or floating-assignment pool, basically users can shift to any v-desktop in the pool.
security features
Horizon Client and Horizon Administrator communicate with a Horizon Connection Server host over secure HTTPS connections.
integrate two-factor authentication for user login
restrict remote desktop access by matching tags in v-desktop pool, but further restriction need design network topology to force certain clients to connect through.